Electric Motors need maintenance regularly in order to avoid failure and prolong their lifespan. Generally, motors and motor parts should be maintained and tested at least every 6 months.
Then only it is possible to maintain a motor’s life and efficiency. We are going to deal with three kinds of maintenance:
- Preventive maintenance – to prevent operating problems and make sure that the motor continuously provides reliable operation.
- Predictive maintenance – to ensure that the right kind of maintenance is carried out at the right time.
- Reactive maintenance – to repair and replace the motor when a failure occurs.
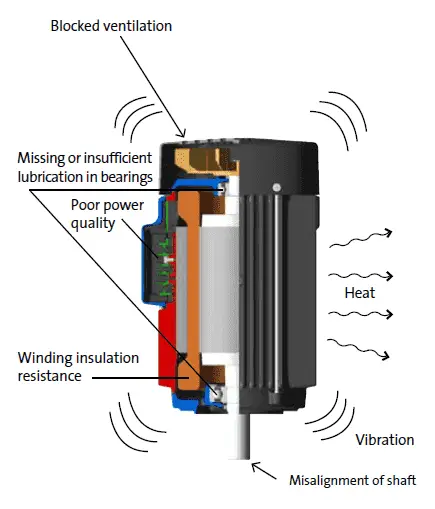
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is electric motor maintenance that is done on a regular basis and can help prevent motors to fail and thus, prevent unexpected production stops. Some of the most important elements included in preventive maintenance are.
- Motor ventilation
- Humidity and condensation
- Loose connections
- Voltage and current imbalance
- Undervoltage and overvoltage
- Bearings, Bearing life, Bearing lubrication
- Lubrication type, Lubrication Intervals
Predictive Maintenance
The objective of predictive maintenance of electric motor maintenance is to reduce maintenance costs by detecting problems at an early stage and deal with them.
- Bearing considerations
- Insulation considerations
- Ground insulation test
- Cleaning and drying stator windings
- Surge test
- High potential testing – HIPOT
- DC high potential ground test
- AC high potential phase to ground test and phase-to-phase test
- Motor temperature
- Thermographic inspection
Reactive Maintenance
When motors fail, it is important to examine the motor and find out where in the motor it happened and why it happened. Normally, good preventive maintenance can prevent failure.
If the failure is caused by a weak component or inadequate maintenance, then all similar equipment has to be examined in order to prevent the same failure from occurring elsewhere in the motor or in the entire system.






Comments are closed.