A utility is a company that generates, transmits, and distributes electricity to its customers. However, not all utilities must offer all three services. The United States has more than 3,200 electric utilities serving over 145 million customers.
These utilities are classified into many types based on the type of ownership. The different types of electric utilities in United States are:
- Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs)
- Public Power Utilities (also known as “Municipals” or “Munis”)
- Cooperatives (Co-Ops)
- Federal Power Programs
- Independent Power Producers
The following sections describe each of the different types of electric utilities in the United States.
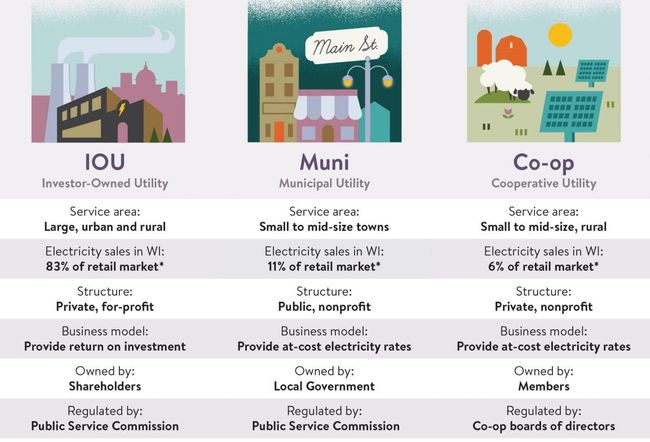
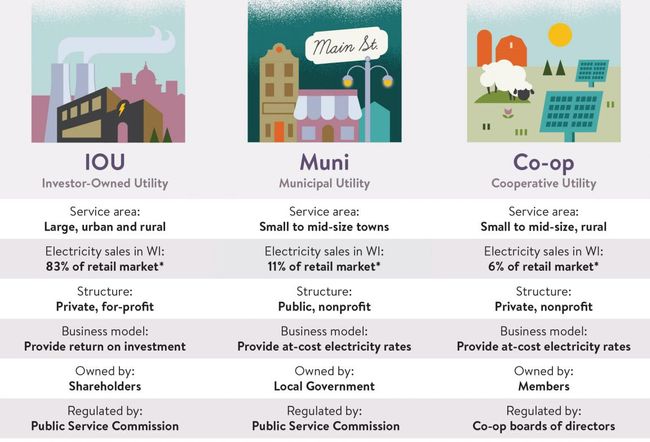
Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs)
An investor-owned utility is a private, monopoly utility that generates and distributes electricity to its customers over a defined service territory. They are for-profit companies owned by their shareholders.
Some of these utilities have service territories across multiple states. State commissions typically license IOUs to operate in specific parts of the state with certain rules and regulations. In addition, FERC regulates their interstate generation, transmission, and power sales while state commissions are responsible for their distribution systems and retail sales.
IOUs are referred to as “monopoly utilities” since they are protected from competition from other providers of electricity by state and federal governments. As a result, IOUs have a secured customer base (all customers who purchase electricity in that service territory) and revenue (your electric bill).
Example of IOUs
| Parent company | Operating company | Operating states |
|---|---|---|
| Black Hills Corporation (BKH) | Cheyenne Light, Fuel & Power | WY |
| FirstEnergy (FE) | Monongahela Power | WV |
| American Transmission Company | American Transmission Company | WI, MI |
| Allete (ALE) | Superior Water, Light and Power | WI |
| Alliant Energy (LNT) | Wisconsin Power and Light | WI |
| Integrys Energy Group | Wisconsin Public Service Corporation | WI |
| MGE Energy (MGEE) | Madison Gas and Electric | WI |
| Wisconsin Energy Corporation | We Energies | WI |
Public Power Utilities
Public Power Utilities (also known as “Municipals” or “Munis”) are not-for-profit utilities owned by cities and counties. Its core mission is to serve local citizens. Utilities owned by cities are referred to as municipal utilities (munis).
Local governments operate public power utilities to provide communities with reliable, responsive, not-for-profit electric service.
Universities and military bases can own and operate their own utilities. These are generally not regulated by FERC or by States, but by their own local government.
Example of Public Power Utilities in California
Alameda Municipal Power -Alameda, CA
Anaheim Public Utilities – Anaheim, CA
Placer County Water Agency – Auburn, CA
Azusa Light & Water – Azusa, CA
Cooperatives (Co-Ops)
Cooperatives (Co-Ops) are not-for-profit entities owned by their members. They must have democratic governance and operate at cost. Members vote for representatives to the co-op’s Board of Directors who oversee operations. Any revenue in excess of costs must be returned to members. Co-ops also tend to serve in rural areas that were not historically served by other utilities.
Electric cooperatives provide energy to booming suburbs as well as remote rural farming communities providing power to 1 in 8 Americans. In Wisconsin, nearly one out every 10 electric consumers is an electric cooperative member. Electric cooperatives are divided into two groups:
Distribution cooperatives are consumer-owned utilities that deliver electricity directly to the consumer.
Generation & transmission (G&T) cooperatives are owned by several distribution cooperatives to furnish their own generating plants and transmission lines to supply power to their member co-ops.
Example
Ag Energy Co-operative
Blue Mountain Power Co-op
Lac La Biche Gas Co-Op
SPARK: Green Energy Alberta
Federal Power Programs
Millions of Americans are served by the federal Power Marketing Administrations (PMAs), which provide them with hydroelectric power produced at federal dams operated by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and the Bureau of Reclamation at cost-based rates.
Federal Power Programs include the
- Bonneville Power Administration (BPA),
- Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA),
- Southeastern Power Administration (SWPA),
- Southeastern Power Administration (SEPA),
- Western Area Power Administration (WAPA).
They provide a range of electric services to other utility companies (mostly municipal utilities), which then distribute to end users. TVA is an independent, Government-owned corporation, but should not be confused with BPA and WAPA, also known as Power Marketing Administrations (PMAs).
BPA and TVA own both generation and transmission facilities. WAPA is a transmission-only utility providing power from Federal hydroelectric facilities in the West to other retail utilities
Independent Power Producer
The Independent Power Producer, or sometimes called a non-utility generator (NUG), is a privately owned business that owns and operates its own generation assets and sells power to other utilities or directly to end users.
NUGs were rare before the enactment of the US Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA) of 1978. The few existing NUGs were seldom able to distribute power, as the cost of building the conveyance infrastructure was prohibitive. Public utilities generated power and owned the generating facilities, the transmission lines, and the local distribution-delivery systems. PURPA, however, established a class of non‐utility generators, called Qualifying Facilities (QFs), that were permitted to produce power for resale.