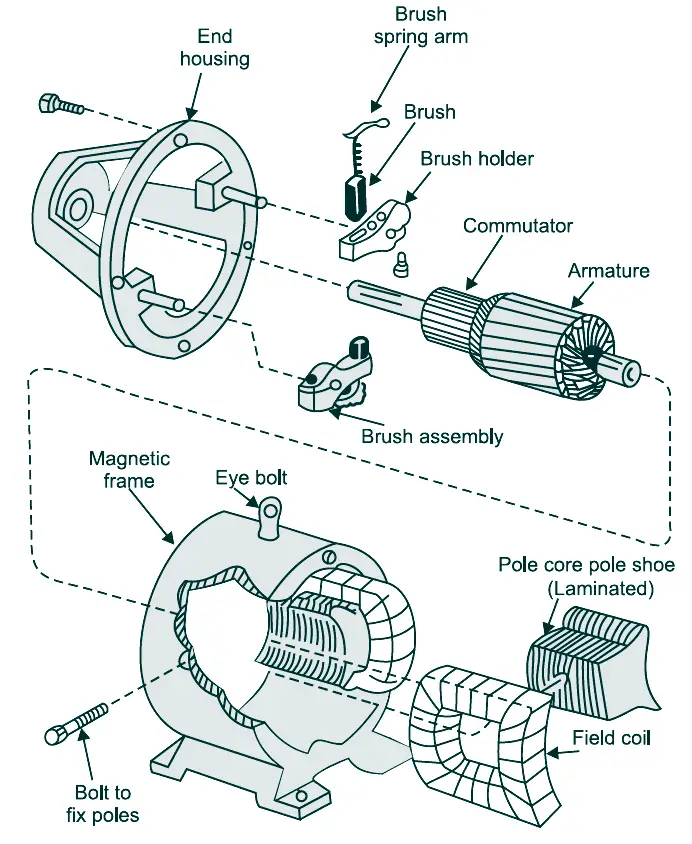
Testing of DC machine is essential too ensure proper fabrication and trouble-free operation of a DC generator and DC motor. By performing these tests, one can determine which machine have the external characteristics needed for the specific application. In addition, the efficiency, rating and temperature rise of the machine can be found.
Some of the important tests on dc machines are:
- Measurement of armature resistance
- Open Circuit Characteristic (OCC)
- Short circuit characteristics (SCC)
- Load test
- Measurement of rotor inertia
- Efficiency of a DC machine
1. Measurement of Armature Resistance
The resistances of field windings and armature windings are measured using the V-I method. In this test, the field winding is not excited. Although any voltage/current value may be used, the highest permissible voltage/current value is chosen during the test to make sure that the error is minimized.
The armature circuit consists of two resistances in series. They are armature winding resistance and resistance due to the brushes and the brush drop.
Brush contact drop behaves similarly to a nonlinear resistance. In order to separate this from the armature circuit resistance and brush resistance, several V-I readings need to be taken.
An equation of V = Vb + IRa form is fitted through these test points shown graphically above.
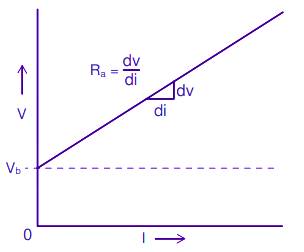
In the case of large values of I, the equivalent armature resistance is equal to V/I ohm. By ignoring the brush drop Vb, the armature resistance Ra equals V/I ohm.
2. Open Circuit Characteristic (OCC)
The Open Circuit Characteristic (OCC) test measures the relationship between the generated voltage and field current under no-load conditions. The test setup involves disconnecting the armature circuit and varying the field current to observe the open-circuit voltage. Key points include:
- A curve plotted between terminal voltage and field current reflects the magnetization curve of the machine.
- The OCC provides information about the saturation behavior of the magnetic circuit and helps determine the voltage regulation of the generator.
3. Short Circuit Characteristic (SCC)
The SCC test assesses the variation of armature current with field current when the armature is short-circuited. Steps include:
- Connecting a low-resistance load across the armature and gradually increasing the field current.
- Recording the short-circuit armature current for corresponding field current values.
- This data helps in understanding the demagnetizing effects and is crucial for fault analysis.
4. Load Test
The load test evaluates the machine under operational conditions to measure its efficiency and performance. Steps involve:
- Connecting variable resistive, inductive, or capacitive loads to the machine.
- Recording armature current, terminal voltage, and mechanical input/output.
- The test provides efficiency curves and helps in validating rated load capacities. Modern techniques, such as dynamometers, are used to measure precise losses and system performance as highlighted in research by Kurtz et al. (Dynamometer Testing).
5. Efficiency Measurement
Efficiency evaluation identifies energy conversion effectiveness and losses. Techniques include:
- Field Tests: Measurements under controlled conditions to determine the operational efficiency of series-wound DC machines, achieving maximum efficiency at specific supply voltages (Sitorus et al., 2014).
- Computational Models: Microcomputer-controlled schemes enable accurate testing with minimal operator interaction (Nagarajan et al., 1990).
These tests ensure that DC machines meet application requirements and operate within their design limits, contributing to improved system reliability and performance.