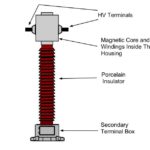
Transformer rating is expressed in kVA, not in kW.
Rating of a transformer or any other electrical machine reflects its load carrying capability without overheating.
Temperature rise (a major threat to insulation) arises due to internal loss within the machine.
An important factor in the design and operation of electrical machines is the relation between the life of the insulation and operating temperature of the machine.
Therefore, temperature rise resulting from the losses is a determining factor in the rating of a machine.
There are two types of losses in a transformer;
- Copper Losses
- Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Copper losses ( I²R) are variable losses which depend on Current passing through transformer windings while Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses depends on Voltage.
We know that copper loss in a transformer depends on current and iron loss depends on voltage. Therefore, the total loss in a transformer depends on the volt-ampere product only and not on the phase angle between voltage and current i.e., it is independent of the load power factor.
So the transformer is designed for rated voltage (iron loss) and rated current (copper loss). We can’t predict the power factor while designing the machine, because the power factor depends upon the load which varies from time to time.
When a manufacturer makes a transformer, UPS etc., they have no idea of the type of load that will be used & consequently they can only rate the device according to its maximum current output that the conductors can safely carry (at unity Power Factor) & the insulation rating of the conductors (voltage & temperature).
That’s why the Transformer Rating may be expressed in kVA, Not in kW.
Related: Why Current Transformer (CT) Secondary Should not be Open?